Package dependency directly from GitHub
- Git
- Npm
- Github
For my projects I often use packages registered in the Npm registry and those are easy to add through the npm install command. But sometimes I want to use my own packages as dependencies. I find it convenient to directly connect to the GitHub repository. The way to do this depends on whether the repository is public or private.
Public GitHub repository
When the repository is public npm can access the repository and it is as simple as using npm install to add the GitHub repository as a dependency.
npm install user/repo#branch
Private GitHub repository
Since a private repositiory is shielded it can only be accessed using a SSH link. To make this work two main steps are necessary.
- a SSH key needs to be created on the machine from where you want to make the connection from;
- the public key of the SSH key needs to be registered to your GitHub account, so GitHub can validate the connection attempt.

To create a SSH key you need a ssh-agent present. Most recent operating systems have it by default installed but if not available it's included for example with Git (Bash). By installing that a ssh-agent should be available.
For more information on SSH go to GitHub Help.
Create a SSH key
In case the ssh-agent is not running, start the agent.
ssh-agent -s
Before you create a SSH key you can check if there already are keys available.
ssh-add -l
If you don't get any identities (keys) back or not one you want to use for this purpose you can generate a new key.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "git@github.com"
The used parameters have the following meaning:
-t = type of key
-b = number of bits in the key
-C = comment (label)
You will be prompted after giving the ssh-keygen command. Answer the questions as desired.
npm i
.
After creating the key, it needs to be added to the ssh-agent newly created identity is registered with the agent.
ssh-add
ssh-add -D
. This will NOT remove the files but only the manually registered identities with the ssh-agent.
Try to connect to GitHub.
ssh -T git@github.com
At this time it will still produce an error "Permission denied (public key)" because we haven't registered the key on our GitHub account yet and therefore authentication will fail.\
When (while creating the key) defaults were used for the key-location, the files that have been generated can be found in the user-directory:
Register public key in GitHub account
Go to your GitHub Settings page, select SSH and GPG keys, and click on New SSH key. Add a descriptive title so you know what the purpose of the key is.
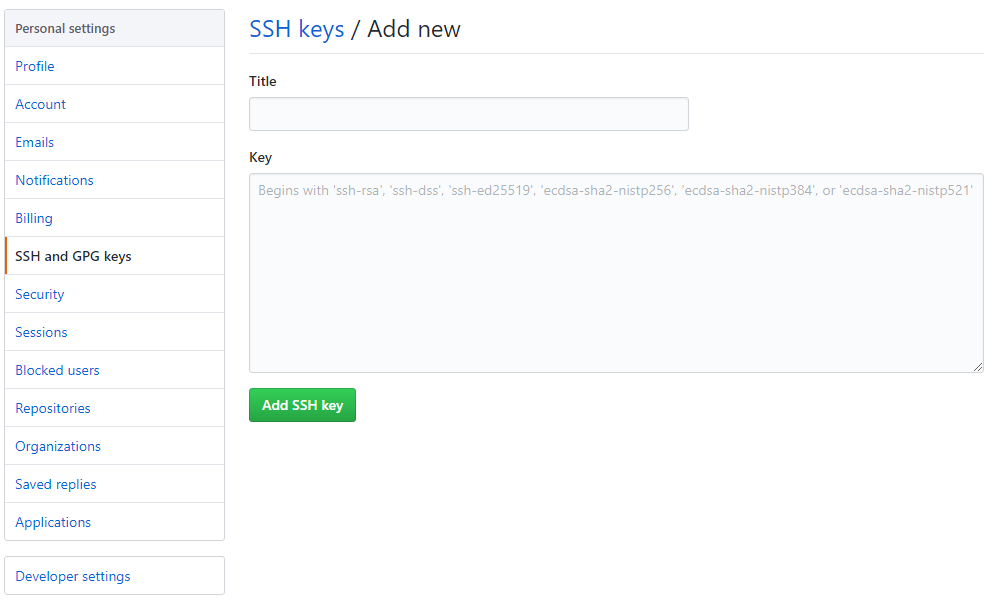
Copy the SSH key to your clipboard.
clip < <path to keylocation>/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
And paste the key in the Key field and click Add SSH key. After that, you should be able to connect to GitHub. Verify the connection.
ssh -T git@github.com
or if you'd like to connect to a specific repo and verify the returned information.
git ls-remote -h -t ssh://git@github.com/<github user>/testrepo.git
This should return the refs/heads and refs/tags of the given repository.
If you still get a "Permission denied" after taking all the steps then check the GitHub Help for possible solutions.
Add package dependency
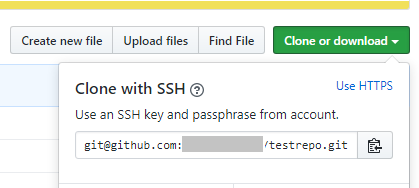
Now all the setup is done you can add the dependency to the package.json. For the address of the dependency just use the ssh-address. You can get this through the clone-copy option in GitHub:
The dependencies of your package.json might look like this:
"dependencies": {
"@custom/test": "git@github.com:your_githubuser/testrepo.git"
}
All that is left to pull in the dependencies into your project from GitHub is npm install.
